The Daily Briefs are a comprehensive update of current affairs for the day. If you’d like to receive updates for current affairs every day, you’ll need to subscribe by entering your email address at the right side of this page. The previous Briefs can be accessed at the archives here.
- The NITI Aayog signed a Statement of Intent (SoI) with Lupin Foundation on July 23, 2018 to collaborate in Aspirational Districts Programme. The SoI was signed by Yaduvendra Mathur, Additional Secretary of NITI Aayog and Sita Ram Gupta, Executive Director of Lupin Foundation. Along with the NITI Aayog, Lupin Foundation will work in three states – Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra and Rajasthan. Lupin Foundation will work towards three main pillars-social, economic and infrastructure-ensuring integrated developmental policies in the model states. Launched by PM Narendra Modi in January 2018, the ‘Transformation of Aspirational Districts’ programme aims to quickly and effectively transform some of the most underdeveloped districts of the country.
- Considering the increasing incidents of mob lynching, the Union Government on July 23, 2018 constituted a High Level Committee chaired by the Union Home Secretary Rajiv Gauba to deliberate in the matter and make recommendations. Alok Srivastava, the Secretary of Department of Justice; Shri Suresh Chandra, Secretary of Department of Legal Affairs; Dr. G. Narayana Raju, Secretary of Legislative Department; and Secretary, Social Justice and Empowerment are the members of the committee.
- The Union Government also constituted a Group of Ministers (GoM) headed by the Union Home Minister Rajnath Singh to consider the recommendations of the High Level Committee. The other members of the GoM are the Union Minister of External Affairs (Sushma Swaraj), Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways (Nitin Gadkari), Union Minister of Law & Justice (Ravi Shankar Prasad) and Union Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment (Thawar Chand Gehlot).
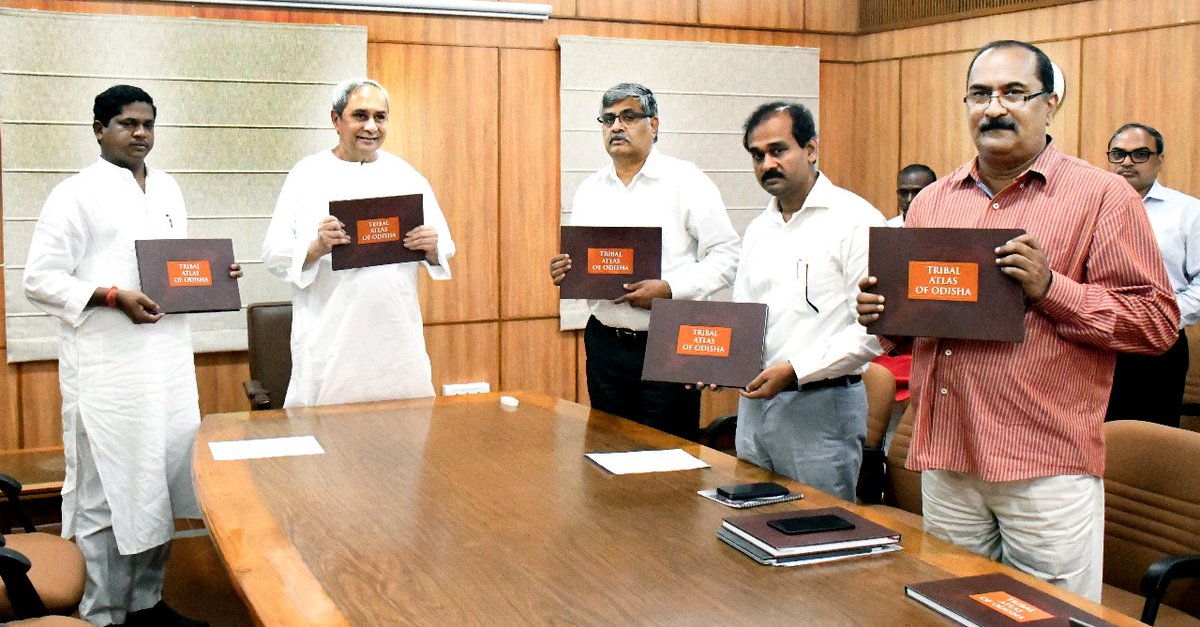

- Odisha Government has unveiled first-ever ‘Tribal Atlas of Odisha’, a compilation of demographic and cultural information of the tribal population in the state. It is claimed to be first-of-its-kind tribal compilation in the country. The book was published by SC and ST Research and Training Institute in collaboration with Academy of Tribal Language and Culture (ATLC). The compendium gives comprehensive and valuable information on tribal regions in state and key demographic indicators like literacy, sex ratio and education. As per Census 2011, Odisha has second highest tribal population in the country after Madhya Pradesh.
- The Lok Sabha on July 23, 2018 passed the National Council for Teacher Education (Amendment) Bill, 2017 that seeks to amend the National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE) Act, 1993. The Bill was introduced by the Minister of Human Resource Development, Prakash Javadekar in Lok Sabha on December 18, 2017. The Bill seeks to grant retrospective recognition to those approved Central and State Institutions and Universities that conduct teacher education courses but do not have recognition under the NCTE Act, 1993.
- The Ministry of Women and Child Development has launched a contest, ‘#Childline1098’ to mark the World Day against Trafficking in Persons on July 30, 2018. The contest invites people to share images of the Childline 1098 logo that they spot at unique locations and send it with a tagline. According to the WCD Ministry, the online contest is a means to connect with the citizens and engage them in spreading information about the initiative towards curbing trafficking. Childline 1098 is India’s first 24-hour, free, emergency phone service for children in need of aid and assistance. The helpline is at present operational at 450 locations.
- India and Rwanda signed eight agreements on July 23, 2018 following delegation-level talks between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Rwandan President Paul Kagame in Kigali, the capital city of Rwanda. Modi and Kagame held wide-ranging talks and discussed a host of measures to boost bilateral strategic ties. The agreements were signed in the fields of defence, trade, agriculture, leather and allied products and dairy. Modi has become the first Indian Prime Minister to visit Rwanda when he landed in Kigali on the first leg of his three-nation- Rwanda, Uganda, Johannesburg-tour to Africa.
- The first meeting of the India-Bangladesh Joint Committee on Border Haats was held in Agartala, Tripura. The Joint Committee also visited Border Haat at Kamlasagar in Sipahijala District, Tripura and Tarapur in Brahmanbaria, Bangladesh. Both sides noted positive impact of Border Haats on livelihoods of people living in areas adjoining Haats. They also held extensive discussions on issues related to review of operations of four functional Border Haats viz. Kalaichar (Meghalaya), Balat (Meghalaya), Kamlasagar (Tripura) and Srinagar (Tripura). Border Haats (or rural market) aims at promoting the well-being of the people dwelling in remote areas across the borders of two countries.
- Unnat Bharat Abhiyan is flagship programme of Ministry of Human Resource Development (HRD) that aims to enrich Rural India. The second edition (Unnat Bharat Abhiyan 2.0) was launched in April, 2018. Currently 748 institutions are participating under the scheme. In phase II, 605 institutions were selected. 143 institutions had taken part in phase-1. The scheme aims to link higher education institutions with set of atleast five villages, so that they can contribute to economic and social betterment of these village communities using their knowledge base.
- Lok Sabha has passed Negotiable Instruments (Amendment) Bill, 2017 to reduce the number of cheque dishonour cases pending in courts. The bill amends Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 to primarily address issues of dishonor of cheques and deal with unnecessary delay in disposal of such cases. The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 defines promissory notes, bills of exchange and cheques.
- Bihar state assembly has passed Bihar Prohibition and Excise (Amendment) Bill, 2018 with 16 amendments to dilute some of stringent provisions in Bihar Prohibition and Excise Act, 2016. The prohibition law was enforced in the state April 2016, banning manufacture, sale or consumption of liquor. No mandatory jail term for first-time offence in case of consumption of liquor. The Bill also watered down penal provision for first-time offenders who store, manufacture or sell liquor from 10-year jail term and Rs 10 lakh fine to 5 year jail term and Rs 1 lakh fine.
Check out the CLATGyan Test Series 2019 : 30 Simulated Online Tests + Personal Mentor | Run entirely by the students of NALSAR University of Law.
Today’s Quiz














THANKS A LOT!!